Leading Pulp and Paper Manufacturing Industry in India

The pulp and paper manufacturer segment in India is one of the largest industries in the country. The sector is an important part of the Indian economy and contributes to the country's GDP.
The industry has an annual turnover of about Rs.50,000 crores as per government estimates. It provides employment to over 2.5 million people directly and about 2 million indirectly through its suppliers, transporters, and other service providers.
Introducing the leading pulp and paper manufacturing industry in India
Shree Varudi Paper Mills is the leading pulp and paper manufacturer in India. It produces high-quality print paper, high BF kraft paper, low GSM kraft papers, and many more products. Shree Varudi is one of the top enterprises in India that provides industrial strength solutions to its customers through innovative products and services.
Shree Varudi has grown over the last few decades as a best-performing company with a proven track record of delivering value to its customers in an ever-changing world.
History of Pulp and Papermaking
Pulp and papermaking in India have a long history. The earliest known use of wood pulp to make paper dates back to the 1st century AD in China. In India, the first reference to papermaking is found in the Vedas, which refer to "papyrus" paper. The earliest reference to pulp and papermaking in India is from the 6th century AD when Chinese monks brought papermaking technology with them from China. It was introduced by Chinese traders into southern India during the 7th century AD after they adopted Buddhism.
India is rich in natural resources like bamboo and cotton that can be used for making various types of paper products including books, writing papers, and packaging materials such as cartons and boxes. Pulp was first made from wood in ancient India. In fact, before wood was used as a raw material for making paper, there were already paper makers in India who used rags or cloth to make their papers.
The earliest known use of wood pulp to make paper dates back to the 1st century AD in China. In India, the first reference to papermaking is found in the Vedas, which refer to "papyrus" paper
The history of pulp and papermaking in India can be traced back to the early 18th century when the British East India Company first established its presence in Calcutta. The company began a paper mill at Howrah, East Bengal, which later came under the control of the Board of Trade. The first Indian paper mill was set up at Hooghly in 1867.
The development of this industry accelerated after India became independent in 1947 with new investments coming from both state-owned and private companies. By 1960, there were more than 100 paper mills operating in India with a total annual production of about 1 million tonnes.
Different Types of Pulp and Paper Products
A sustainable and recyclable raw material derived from trees is pulp. Because it is among the most adaptable resources available, the pulp has a multitude of purposes, from the commonplace (like tissues, publications, and baby wipes) to the cutting-edge (like vehicle filtration, LCD screens, sustainable energy, and tags).
Bills, post-its, postcards, disposable cups, tablecloths, swabs, cartons, nappies, baby wipes, purses, meal wrappers, separators, bonding compounds in food and medicines, labeling, and stamps are all examples of pulp and paper-based product offerings.
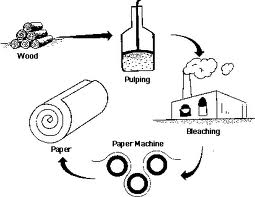
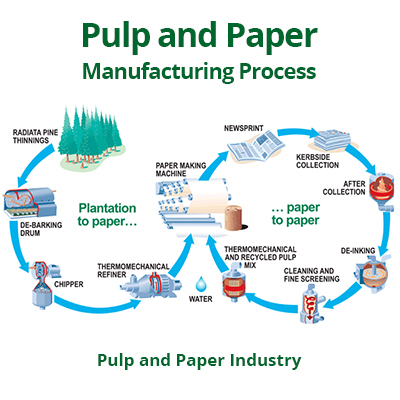
How Pulp and Paper are made?
The pulp and paper-making process begins with the collection of raw materials from the forest. These raw materials include trees (lignin), fibers (cellulose), and water. The pulp is then placed in a press, which compresses the pulp into a pellet. This pellet is then dried and ground into fibers. The fibers are separated from each other by washing.
The cellulose fibers are placed in a press that squeezes out the lignin from them. This new product is called "wood pulp" or "fiber." The fiber can be used for many different products, including paper, packaging, textiles, or insulation. The lignin can be used as fuel, while the cellulose can be used as animal feed or as industrial products like insulation or packaging material.
Fibers are separated from each other by passing them over rollers that beat them against other rollers in order to create individual fibers. These individual fibers are then wound onto bobbins that allow them to be stored until required for use in papermaking.
Highlight Recent Advancements in the Pulp and Paper Industry
Sustainable growth is the most significant trend now affecting pulp and paper manufacturers. For several top businesses, it is currently a need. The tastes have changed throughout the previous few years. The regulatory landscape is evolving quickly as various environmental standards are introduced globally. The paper sector is up against a formidable challenge, not just in terms of profitability. As ecological problems have gained popularity, sustainable techniques have had to overcome difficult obstacles.
Packaging can advance by utilizing technological advancements like virtual reality or machine intelligence. Deep learning may enhance the quality and upkeep of products, which would be a game-changer for industrial optimization.
Environmental impact of pulp and paper production
The pulp and paper sector will confront significant challenges ahead as sustainability goals are becoming more stringent and practical needs don't just have to be profitable. Sustainability benchmarking must be viewed as an encouragement to combine financial, ecological, and social responsibilities. In its most basic form, pulp and paper making is a sustainable process.
The advantages of the modern pulp and paper production process are that it doesn't use as much energy as other methods of making pulp or paper; it produces a cleaner product than some other methods, and it produces a consistent quality product every time.
Shree Varudi Paper Mills has been a benchmark in modern sustainable manufacturing. As a leading pulp and paper manufacturer, we have committed our operations, ethics, and goals to a greener solution.
For more information -
Contact us : +91 94848 22222
Email us : sales@shreevarudi.com